Nepal Scoping Review
Investigating baseline water quality to pinpoint interventions and future improvements
Project Leads: Dr. Leena Malayil; Dr. Suhana Chattopadhyay
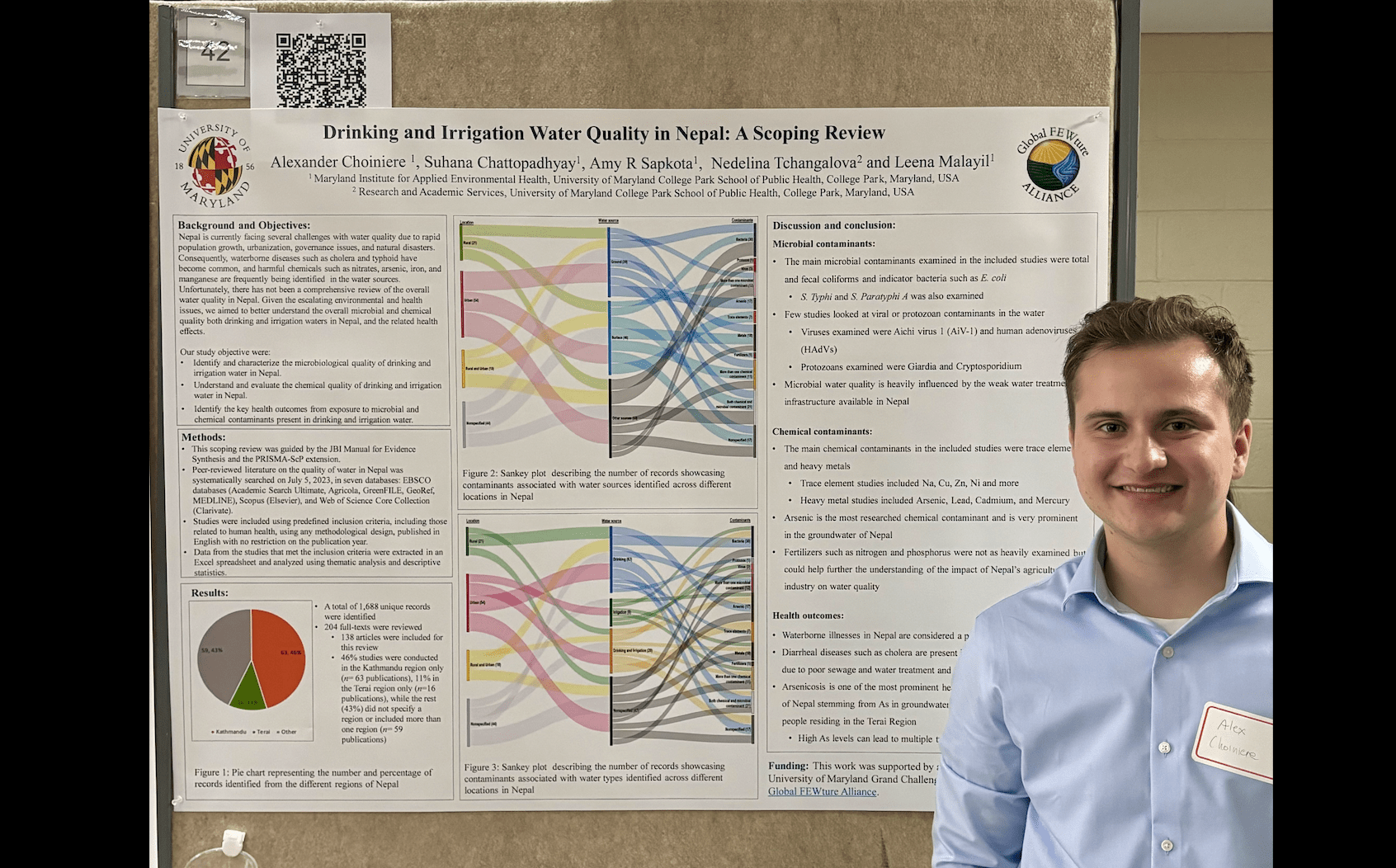
Nepal faces several challenges with water quality due to rapid population growth, urbanization, governance issues, and natural disasters. Consequently, waterborne diseases such as cholera and typhoid have become common, and harmful chemicals such as nitrates, arsenic, iron, and manganese are present in the water sources.
Unfortunately, there has not been a comprehensive review of the overall water quality in Nepal. Therefore, we have conducted a scoping review to gain a better understanding of the quality of both drinking and irrigation waters. This study is crucial in identifying key areas that need to be addressed to achieve improved water quality in Nepal, which will safeguard the health of its citizens.
For our review publication, Microbial and Chemical Water Quality Assessments Across the Rural and Urban Areas of Nepal: A Scoping Review, we reviewed 140 studies that met our criteria. They encompassed a variety of methodological designs, with the majority focusing on water sources in the Bagmati province. Bacteria and arsenic emerged as the most prevalent contaminants. Diseases such as arsenicosis and typhoid remain widespread and may be linked to contaminated water sources.
The review identified key gaps in Nepal’s water quality management, including limited geographic research coverage, inconsistent testing protocols, weak regulatory enforcement, and a lack of integration of water quality with public health planning. Our findings underscore the urgent need for effective surveillance systems and a robust regulatory framework to promptly respond to water contamination events in Nepal.
Fulfills Global FEWture Alliance Objective: